Adjustable Speed Drives –
(a.k.a. Variable Speed Drives)
What They Are, How They Work
Application Information
- Adjustable Speed Drives – Application Information
- DC Drives – Principles of Operation
- DC Drive Types
- DC Motor Control Characteristics
- AC Drives – Principles of Operation
- AC Controller Types
- AC Motor Control Characteristics
- Motor Selection
- AC vs. DC Drive Comparison
- Basic Mechanics
- Other Application Factors
- Measuring Machine Torque
- Mechanical Formulas
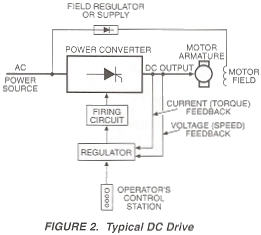
DC DRIVES – PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
DC drives, because of their simplicity, ease of application, reliability and favorable cost have long been a backbone of industrial applications. A typical adjustable speed drive using a silicon controller rectifier (SCR) power conversion’ section, common for this type unit, is shown in Figure 2. The SCR, (also termed a thyristor) converts the fixed voltage alternating current (AC) of the power source to an adjustable voltage, controlled direct current (DC) output which is applied to the armature of a DC motor.
SCR’s provide a controllable power output by “phase angle control”, so called because the firing angle (a point in time where the SCR is triggered in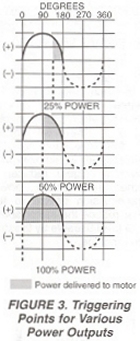
Adjustable Speed Drive Application Information provided by: FINCOR Automation